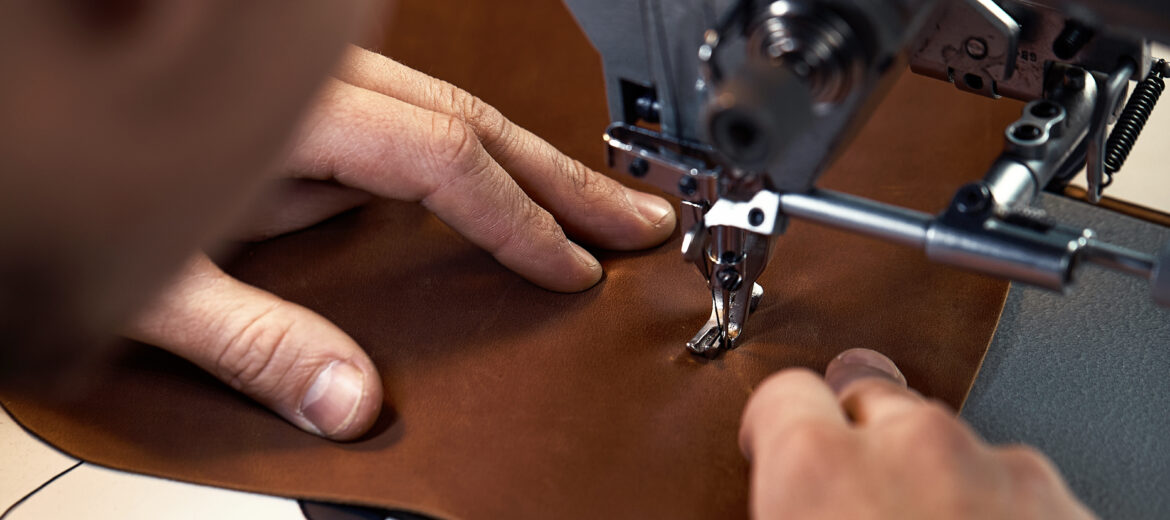
Ethical Leather Production
As sustainability becomes a key focus in various industries, ethical leather production and green energy integration are transforming the way we approach manufacturing. Ethical leather production prioritizes humane animal treatment, responsible sourcing, and eco-friendly tanning methods. Traditional leather production relies on chemical-heavy processes that pollute water sources and harm ecosystems. In contrast, ethical leather manufacturing emphasizes vegetable tanning, water-efficient techniques, and byproduct utilization to minimize waste and environmental impact. Additionally, alternative leather options, such as plant-based and lab-grown leather, are emerging as sustainable solutions.
Green energy integration plays a crucial role in reducing the environmental footprint of leather production. Factories and tanneries are increasingly adopting solar, wind, and biomass energy to power operations, significantly reducing carbon emissions. Energy-efficient machinery and wastewater treatment plants further enhance sustainability efforts. By incorporating renewable energy sources, manufacturers can lower reliance on fossil fuels, cut operational costs, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
The combination of ethical leather production and green energy ensures a responsible approach to fashion and manufacturing. As consumers demand greater transparency, businesses must embrace these practices to create high-quality, sustainable leather products while protecting the planet. The future of leather lies in innovation, ethics, and clean energy solutions.
Challenges
Despite advancements in ethical leather production and green energy integration, several challenges persist in the industry:
High Production Costs – Ethical tanning processes and renewable energy solutions require significant investment, making them costlier than traditional methods.
Limited Consumer Awareness – Many consumers are unaware of the environmental impact of conventional leather and the benefits of sustainable alternatives, slowing market adoption.
Sourcing Ethical Raw Materials – Ensuring that animal hides are ethically sourced and free from exploitative practices remains a major challenge.
Energy Infrastructure Limitations – Many leather production facilities lack the necessary infrastructure to integrate solar, wind, or biomass energy effectively.
Regulatory Compliance – Adhering to environmental laws, waste management policies, and labor standards requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to evolving regulations.
Technological Barriers – Innovations like lab-grown leather and plant-based alternatives require further development and scaling before they can become mainstream.
Supply Chain Transparency – Ensuring traceability from raw materials to finished products is complex and requires robust monitoring systems.
Market Competition – Traditional leather producers using cheaper, less sustainable methods still dominate the industry, making it difficult for ethical producers to compete.
Consumer Price Sensitivity – Ethical leather and green energy-based products often come at a premium price, which some consumers may be unwilling to pay.
Waste Management – While ethical practices reduce environmental impact, managing byproducts and ensuring efficient resource use remains an ongoing challenge.
Similar Projects

Community Empowerment Initiatives
The majority have suffered alteration in some form, injected humour.